Answer: Option (D) is the correct answer.
Step-by-step explanation:
An equilibrium reaction is defined as the reaction in which concentration of both reactants and products are constant.
For example,
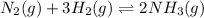
In a dynamic equilibrium, rate of forward and backward reaction are continuous.
So, rate for this reaction will be as follows.
Rate =
![([NH_(3)]^(2))/([N_(2)][H_(2)]^(3))](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/8bwoom7x35fb61qvj8ar6awi1ezcotbkuz.png)
When rate of forward reaction is equal to rate of backward reaction then it is known as reversible reaction.
Thus, we can conclude that the statement concentration of reactants and the concentration of products are constant, is true of a reversible reaction at equilibrium.