Let us first calculate heat obtained by the evaporation of 51 g of water.
Given, heat of vaporization of water = 2.4 kJ/ g
∴ Heat obtained by evaporation of 51 g of water = 2.4 × 51 = 122.4 kJ
This is the heat energy available that can be used to cool water from 42°C to 20°C.
Specific heat of water is given by,
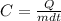
Here,
C is the specific heat of water = 4.18 J/gK
Q is the amount of heat = 122400 J
m is the mass of the water that can be cooled.
dt is the change in temperature= 42°C ₋ 20°C = 22°C ( The numerical value will be the same if Kelvin unit is used.)
Substituting the values we get,
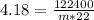
m = 1331 g
1331 grams of water can be cooled from 42°C to 20°C by evaporation of 51 g of water.