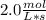Answer : The correct answer for rate of consumption of B =
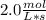
Dynamic equilibrium :
Dynamic equilibrium is state of equilibrium where reactants convert to product and product converts to reactant at equal and constant rate . The concentration may not be same but rate will be same .
This occurs when reaction is reversible type .
The hypothetical reaction is :
A ↔ B where ↔ represents reversible reaction
Rate of consumption of A is given as :
![R(a) = k * (d[A])/(dt)](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/high-school/7g2p2gis5ani7rl81nnsl05ilttmp13xbe.png)
Where . R(a) = rate of consumption of A
k = rate constant
[A] = concentration of A
t= time
Rate for consumption of B =
![R (b)= k * (d[B])/(dt)](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/high-school/e1f7t71fl83gn6udk6lru48u60uzb4lbvh.png)
R(b) = rate of consumption of B , [B] is concentration of B
Since the reaction is at dynamic equilibrium , so :
Rate of consumption of A = rate of consumption of B
Given : rate of consumption of A =
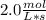
Hence rate of consumption of B =