Answer:
C and E
Step-by-step explanation:
The answer is:
- Gravitation between two objects increases when the distance between them decreases.
- When the mass of an object increases, its gravitational pull also increases.
And it is all explained with one formula: the Newton's Universal Law of Gravity:
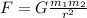
Where F is the gravitational force or pull, G is the gravitational constant, m means mass and r is the distance between the two objects.
In the moments after the big bang, the atoms in gas clouds were gathering together forming what we know now as galaxies, meanwhile as expansion was continuing, the distance between atoms in other regions of the universe was increasing. If we look at Newton's law, the square of the distance is inversely proportional to the Gravitational Force, so, as the distance increases, the Gravitational Force decreases.
On the other matter, now with gravitational force increasing in gas clouds, the cumulative mass of atom groups inside said gas clouds was increasing, while atoms in other part of the universe, being apart, suffered no cumulative increase of mass. Again, looking at the formula, if either
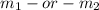 increases, them being directly proportional to F, if the mass increases the gravitational pull also increases.
increases, them being directly proportional to F, if the mass increases the gravitational pull also increases.