Answer:
current will DECREASE in the circuit while equivalent resistance will INCREASE for the circuit
Step-by-step explanation:
If three resistors are connected in parallel then in that case the equivalent resistance of all three is given by
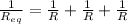
so here we can say
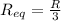
now the current in the circuit is given as
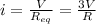
now if one of the resistance is removed from it
now the equivalent resistance is given as
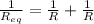
so it is given as
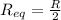
now the current in the circuit is given as
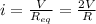
So current will DECREASE in the circuit while equivalent resistance will INCREASE for the circuit