The equation is given as
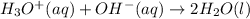
We have been given the standard free energy , ΔG° = -79.9 kJ
The relationship between standard free energy, ΔG° and equilibrium constant K is given by the following equation.
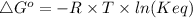
Here ΔG° is standard free energy in J
We have,
ΔG° = -79.9 kJ = -79900 J
T = Temperature in Kelvin = 25 + 273 = 298 K
R = Gas Constant = 8.314 J/mol K
Let us plug in these values in above equation.
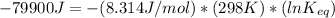
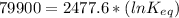
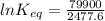
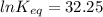
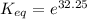
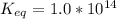
The equilibrium constant for the given reaction is 1.0 x 10¹⁴