Answer :The correct answers are :
Concentration in one can soup : Table salt = 6.12
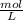
Table sugar = 5.84
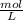
Concentration in one bowl Soup : Table salt = 3.82
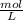
Table sugar = 3.65
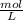
Concentration : It is quantity to measure a solution . It can be defined as abundance of constituents per volume of solution . The most used concentration is molar concentration .
Molar concentration is defined as mole of solute present in volume of solution . The unit of concentration is
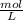 . It is expressed as :
. It is expressed as :

Concentration in one can of soup (Volume = 250 mL )
Volume of one can soup = 250 mL . Converting it from mL to L as :
(1 L = 1000mL)
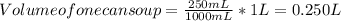
A) Concentration of table salt :
Following are the steps to find out molar concentration :
Step 1 : Find mass of solute :
Since mass of solute is not given , so we take solubility of NaCL in 1 L of water . Solubility is maximum amount of NaCL that can be dissolved in 1 L water at room temperature . From image , we can say that 359 g of NaCL can be dissolved ideally in 1 L of water .
Since volume of solution is 0.250 L , so mass of salt in 0.250 L can be found :
Mass of NaCL in 1 L = 359 g
Mass of NaCL in 0.250 L of water = 359 g * 0.250 L
Mass of NaCL in 0.250 L = 89.75 g
Step 2 : Convert mass of solute to its mole
Mole can be calculate from mass as :
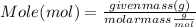
Molar mass of Table salt (given ) = 58.44
plugging value of mass and molar mass in mole formula :
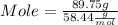
Mole of Table salt = 1.53 mol
Step 3 : To find concentration .
Mole of solute = 1.53 mol
Volume of solution ( one can of soup ) = 0.250 L
Plugging these values in Concentration formula :
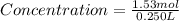
Concentration of Table salt in one can soup = 6.12
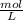
B) Concentration of Table sugar :
Following steps can be used :
Step 1: To find mass of Table sugar
Since mass of sugar is not given , so solubility of sugar will be considered . From image solubility is 2000 g in 1 L of water .
Since volume of one cup soup is 0.250 L , so mass of Sugar in 0.250 L of solution =
Mass of sugar in 1 L of water = 2000 g
Mass of sugar in 0.250 L of solution = 2000 g* 0.250 L
Hence , mass of Sugar in 0.250 L of solution = 500 g
Step 2 : To convert mass of sugar to its mole
Mass can be converted to mole using same formula. Plugging value in mole formula :
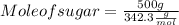
Mole of sugar = 1.46 mol
Step 3 : To find concentration of Sugar :
Mole of sugar = 1.46 mol
Volume of solution = 0.250 L
Plugging these values in concentration formula :
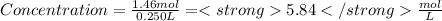
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Concentration in one bowl of soup :
Volume of one bowl of soup = 150 mL water + 250 mL of one can soup
= 400 mL
Converting mL to L : ( 1 L = 1000mL )
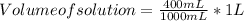
Volume of solution = 0.400 L
A) Concentration of Table salt :
Similar steps will be used :
Step 1: T find mass of Table salt
Again solubility will be used , which is =359 g in 1 L .Since 150 mL water is added which had no salt . hence all the salt was present in 250 mL one can soup , so mass of salt present in one can soup will be used .
Mass of Table salt = 89.75 g
Step 2: To convert mass to mole
Mass can be converted using mole formula .
Mole of Table salt = 1.53 mol ( calculated above )
Step 3: To find concentration
Mole of Table salt = 1.53 mol
Volume of one bowl soup = 0.400 L
Plugging these values in Concentration formula as:
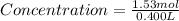
Concentration of Table salt in one bowl soup = 3.82
B) Concentration of Table sugar :
Step 1 : To find mass of Table sugar
Mass of sugar in 0.400 L will be same as that of mass of sugar present in 0.250 L since water had no sugar .
Mass of Table sugar = 500 g
Step 2 : To convert mass to mole
Mole can be calculated using mole formula ( as calculated above for one can soup )
Mole of Table sugar = 1.46 mol
Step 3: To find concentration
Mole of Table sugar (solute ) = 1.46 mol
Volume of one bowl soup = 0.400 L
Plugging these values in concentration formula :
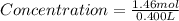
Concentration of Table sugar in one bowl soup = 3.65
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Also Note :You have marked Table sugar as Ionic which is incorrect .Table sugar is covalent as it has all non metals .