Given information : H = -92 KJ/mol and S = -0.199 KJ/(mol.K)
At equilibrium G = 0
We have to find the Temperature at which reaction would be spontaneous.
For spontaneous reaction :
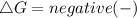
For non-spontaneous reaction :
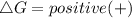
We can find the temperature using the formula for Gibbs free energy which is:
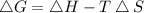
Where, G = Gibbs free energy ,
H = Enthalpy
S = Entropy
T = Temperature
By plugging the value of G , H and S in the above formula we can find 'T'
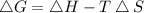
Since reaction should be spontaneous that means
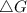 should be negative , so the above formula can be written as :
should be negative , so the above formula can be written as :
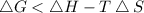
On rearranging the above formula we get :
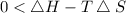
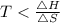
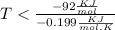
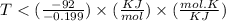
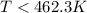
For the reaction to be spontaneous , T should be less than 462.3 K, so out of given option , C is correct which is 400 K.