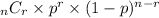1. There must be exactly two possible outcomes (girl, boy).
2. Repeated trials must be independent.
3. The probabilities of the two outcomes don't change from trial to trial.
n = 3 (there are 3 children "generated")
p = 0.55 (the probability that a child is a girl)
The probability that a family of 3 consists of one girl and two boys is
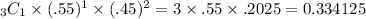
In general, the probability that a binomially distributed random variable X is equal to r is