The chemical properties of an organic compound are governed by the functional groups present in that compound. The different types of functional groups are ketones, amines, alcohols, esters and carboxylic acids.
The formulas of some functional groups
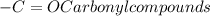
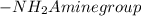
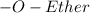
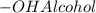
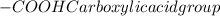
Therefore, amines contain nitrogen atoms bound to one, two, or three carbons.