Answer : the correct answer for ksp = 1.59 * 10⁻⁹
Following are the steps to calculate the ksp of reaction
BaCO₃ →Ba ²⁺ + CO₃²⁻ :
Step 1 : To find ΔG° of reaction :
ΔG° of reaction can be calculates by taking difference between ΔG° of products and reactants as :
ΔG° reaction =Sum of ΔG° ( products ) - Sum of Δ G° ( reactants ) .
Given : ΔG° for Ba²⁺ ( product )= -560.7
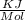
ΔG° for CO₃²⁻ (product ) =- 528.1
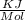
ΔG° BaCO₃ ( reactant) = –1139
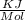
Plugging value in formula :
ΔG° for reaction = ( ΔG° of Ba ²⁺ + ΔG° of CO₃²⁻ ) - (ΔG° of BaCO₃ )
⁻ = ( -560.7
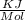 + 528.1
+ 528.1
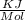 ) - ( -1139
) - ( -1139
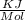 )
)
= ( -1088.8
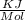 ) - (-1139
) - (-1139
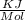 )
)
= - 1088.8
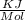 + 1139
+ 1139
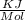
ΔG° of reaction = 50.2
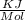
Step 2: To calculate ksp from ΔG° of reaction .
The relation between Ksp and ΔG° is given as :
ΔG° = -RT ln ksp
Where ΔG° = Gibb's Free energy R = gas constant T = Temperature
Ksp = Solubility constant product .
Given : ΔG° of reaction = 50.2
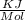
T = 298 K R = 8.314
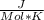
Plugging values in formula
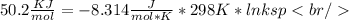
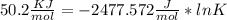
((Converting 2477
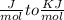
Since , 1 KJ = 1000 J So ,
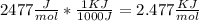 ))
))
Dividing both side by
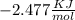
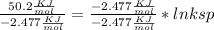
ln ksp =
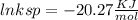
Removing ln :
ksp = 1. 59 * 10⁻⁹