Oxidation is a process in which electrons are lost from the substance. Since electrons are lost, oxidation state increases.
In the above reaction, we can see that oxidation state increases for Mn from 0 to +2. That mean Mn is undergoing oxidation.
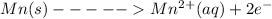
We have
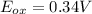
The oxidation state decreases for Cu, that means Cu undergoes reduction.

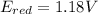
The formula to calculate cell potential is
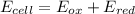
Let us plug in the given Eox and Ered values.
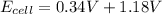

The overall cell potential is +1.52V