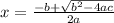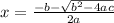Firstly we learn the standard quadratic equation,
ax²+bx+c=0
where a,b,c are real numbers.
Now solve the quadratic equation using the Complete the square method.
Rewriting part of the equation as a perfect square trinomial. If you complete the square on the generic equation ax² + bx + c = 0 and then solve for x,
ax²+bx=-c
x² +
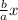 =-c
=-c
add both the side
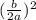
x² +
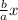 +
+
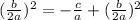
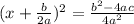 `
`
take square root both the side