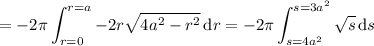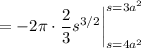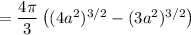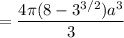The amount of material removed is the volume of the region within the sphere bounded by the cylinder. Consider a sphere of radius
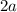 centered at the origin; this sphere has equation
centered at the origin; this sphere has equation

The given cylinder has equation
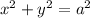
The volume of the region of interest
 is given by
is given by
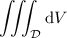
Converting to cylindrical coordinates, setting
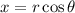
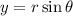
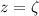
we have
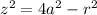
and
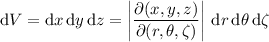
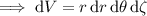
where
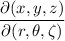 is the Jacobian of the transformation from
is the Jacobian of the transformation from
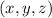 to
to
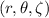 . The region
. The region
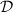 is described by the set
is described by the set
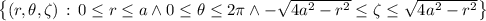
The integral is then
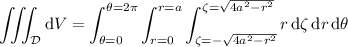
The integral with respect to
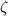 is symmetric about
is symmetric about
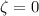 , so we instead compute twice the integral from
, so we instead compute twice the integral from
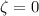 to
to
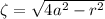 , and we can immediately compute the integral with respect to
, and we can immediately compute the integral with respect to
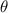 :
:
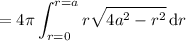
Now, let
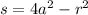 , so that
, so that
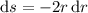 :
: