ice:
mass (m) = 1 kg
Initial Temperature (T) = 0 ° C
Latent heat (L) = 3.34 * 105 J/kg
Water:
mass (m) = 9 kg
Initial Temperature (T) = 50 ° C
Specific heat capacity (c) = 4,160 J/kg
First you must find the amount of heat required for the ice to turn into water (Q is heat)
Q = mL
Q = 1 * ( 3.34 *
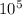 )
)
Q = 3.34 *
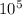 J
J
1 kg of ice needs 3.34 * J of energy to convert into water
The heat lost by the water is equal to the heat gained by the ice.
Heat can be found using the equation: Q = mcΔT therefore...
mcΔT (water) = mcΔT (ice)
9 * 4,160(50 - x) = 1 * 4,160(x - 0) + 3.34 *
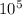
You need to add the heat needed for the ice to convert into the water (3.34 *
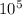 J) to the ice side of the equation, because when we get the final temperature the ice will be converted into water.
J) to the ice side of the equation, because when we get the final temperature the ice will be converted into water.
x = 36.97
The resulting temperature is 36.97 ° C
I hope this helped!
~Just a girl in love with Shawn Mendes