Step-by-step explanation:
It is given that volume is 7.68 L, temperature is 355 k and pressure is 8.57 atm. So, according to ideal gas equation PV = nRT.
Also, it is known that number of moles equal mass divided by molar mass.
Therefore, putting the given values into the ideal gas equation as follows.
PV = nRT
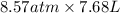 =
=
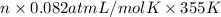
n = 2.26 mol
Thus, we can conclude that the number of moles present in given oxygen is 2.26 mol.