Step 1 : Write balanced chemical equation
The balanced chemical equation for the reaction between iodine gas and chlorine gas is given below.

Step 2 : Set up ICE table
We will set up an ICE table for the above reaction
Following points are considered while drawing ICE table
- The initial concentration of product is assumed as 0
- The change in concentration (C) is assumed as x. Change (x) is negative for reactants and positive for products
- The coefficients in balanced equation are considered while writing C values
Check attached file for ICE table
Step 3 : Set up equilibrium constant equation
The equation for equilibrium constant can be written as
![K_(eq) = ([ICl]^(2))/([I_(2)][Cl_(2)])](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/9rl03pk75zandb374v1bu6hcbbn2cat4hg.png)
Step 4 : Solving for x
Keq at 298.15 K is given as 81.9
Let us plug in the equilibrium values (E) for I₂, Cl₂ and ICl from ICE table
81.9 =
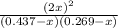
81.9 =
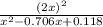
![(2x)^(2) = 81.9 [ x^(2) -0.706x + 0.118]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/ar8riynahsh3qb18eibxt1javpiqrze63w.png)
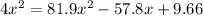
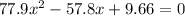
Solving the above equation using quadratic formula we get
x = 0.488 or x = 0.254
The value 0.488 cannot be used because the change (C) cannot be greater that initial concentration of the reactants.
Therefore the change in concentration of the gases during the reaction is 0.254 M
Hence, x = 0.254 M
From the ICE table, we know that the equilibrium concentration of ICl is 2x
![[ICl]_(eq) = 2 ( 0.254) = 0.508 M](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/mlr8lp7bpd31lpv7zp8zxtsdjkrpk73cxm.png)
The concentration of ICl when the reaction reaches equilibrium is 0.508 M