When we know the roots are r and s we can just multiply (x-r)(x-s) and set it to zero to recover the original quadratic equation. We can then scale to get rid of fractions or common factors if we like.
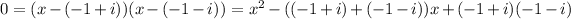
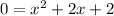
The linear term coefficient is negative the sum of the roots, which in the case of conjugates is (negative) twice the real part, coefficient +2 here. The constant term is the product of the roots, which in the case of conjugates is the squared magnitude, here
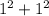 .
.
We got a 2x in the middle so we get
Answer: 2x