General Idea:
Experimental probability refers to the probability of an even occurring when an experiment was conducted and data was produced detailing the number of times an even occurred. Experimental probability is found by repeating an experiment and observing the outcomes.
P(event) = Number of times event occur/Total number of trials
Applying the concept:
The experimental probability of the cup landing on its open end =
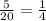
The experimental probability of cup landing on its closed end =
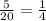
Conclusion:
The statement which best compares the experimental probability of the cup landing on its open end with the experimental probability of the cup landing on its closed end is option A.
The probabilities are equal.