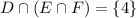We can easily enumerate E and F:

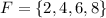
The intersection
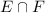 is a set composed by all the element belonging to both E and F, i.e. 4.
is a set composed by all the element belonging to both E and F, i.e. 4.
The intersection of this set with D works in the same way, but it's actually a trivial one, since
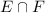 is a subset of D. In fact, D is the set of all integers, while 4 is a particular integer. And in general, if A is a subset of B, then the intersection between A and B is A itself, so the final answer is
is a subset of D. In fact, D is the set of all integers, while 4 is a particular integer. And in general, if A is a subset of B, then the intersection between A and B is A itself, so the final answer is