The law of partial pressures or Dalton's law, formulated the British chemist John Dalton in 1802, establishes that the pressure of a mixture of gases, that do not react chemically, is equal to the sum of the partial pressures that each of them would exert if only one occupied the entire volume of the mixture, without changing the temperature.
In this way, Dalton's law can be used to determine the total pressure in a container that has a mixture of gases, each of which exerts a partial pressure, considering that all gases behave like ideal gases.
According to Dalton's law, the total pressure in the flask will be,
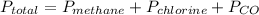
→
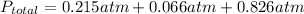
→
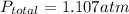
So, the total pressure in the flask is equal to 1.107 atm.