Answer:
Option B.
Explanation:
The given function is
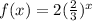
From the given table we can say when we increase x by 1 (from 0 to 1) value of function is
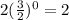
Now we increase x by 1 (from 1 to 2) then value of the function will be
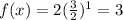
Therefore we see the common ratio of the function value is 3/2 = 1.5
Similarly for the other values of x = 2, 3 we find he value of the function = 4.5, 6.75
Which shows the common ratio as 1.5 for every value of the function.
So we conclude with the increase of x function increases by at a constant multiplicative rate.
Option B is the answer.