1) The velocity of the particle is given by the derivative of the position. So, if we derive s(t), we get the velocity of the particle as a function of the time:
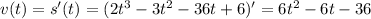
2) The acceleration of the particle is given by the derivative of the velocity. So, if we derive v(t), we get the acceleration of the particle as a function of the time:
