Each sample of Shelia's glucose comes from a normal distribution with mean 128 and standard deviation 10. The average of three samples is normal with the same mean and a standard deviation of
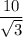 .
.
By the 68-95-99.7 rule a one sided probability of 2% is a bit more than two standard deviations above the mean (2.5%). We look up 1-.02=.98 in the normal table that's the integral of the standard normal from 0 to z and get z=2.06.
For the observed average to have probability 2% it needs to be 2.06 standard deviations above the mean, so
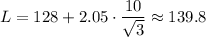
Part a: 139.8
For the sample average compared to 140, we compute how many standard deviations 140 is above our mean of 128.
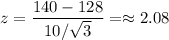
That's virtually the same as the last result, but we look it up and get .98124, so p=1-98124=.019.
Part b: .019