Answer:
The four fundamental forces magnitude and range are in order of Strong Nuclear Force > electromagnetic force > weak nuclear force > gravitational force.
Step-by-step explanation:
The 4 fundamental force are weak nuclear force, strong nuclear force, em force and the gravitational force are discussed below.
- Strongest force is the strong nuclear force as compared to all of them. It is very useful for capturing the atoms nucleus together despite the large repulsion which is occur between the same charges due to protons in the nucleus.
- Electromagnetic Force is the 2nd strongest fundamental force. Magnetism and electricity was thought to be of 2 separate forces.
- Weak Nuclear Force involves the W and Z bosons exchange. It has a very short range of
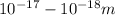
- Gravitational Force is the weakest between all the fundamental forces. However, due to its long range it is the most dominant force. It follows the inverse square law like but it is always attractive in nature.