Answer: Option (D) is the correct answer.
Step-by-step explanation:
Alkanes are the hydrocarbons which contains only single bonds to join its corresponding atoms with each other.
In general, formula of an alkane is
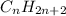 where n is a whole number.
where n is a whole number.
This general formula is applicable only for alkanes which are linear and branched in nature.
In linear alkane, atoms are attached in a chain like structure.And, in a branched alkane there will be presence of branches in the form of groupls like methyl, ethyl etc.
In cyclic alkanes, there will be single bonds between carbon and hydrogen atoms but the carbon atoms will bond together in the form of a ring. In a cyclic alkane, the number of hydrogen atoms will be less than the number of hydrogen atoms present in a linear or branched alkane.
So, in the given structure carbon atoms are attached to each other in the form of a ring. Hence, it is a cyclic alkane with less number of hydrogen atoms as compared to a linear alkane with a chain of 6 carbon atoms.
Thus, we can conclude that the number of hydrogen atoms is the property which differentiates this alkane from other classes of alkanes.