Answer:
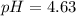
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello!
In this case, since the ionization of ammonia, which is a weak base, is written as:
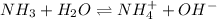
We can see that the ammonium ion is the conjugate acid whereas the hydroxide ions the conjugate base; that is why we use the Henderson-Hasselbach equation to compute the pH, given the pKb of ammonia 4.75:
![pH=pKb+log(([conj\ acid])/([base]) )](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/o4vvih79uphtoqivo4hetx1jly8ymhodix.png)
In such a way, for the given moles of ammonia, base, and those of ammonium chloride, conjugate acid form, we obtain:
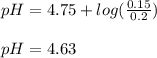
Best regards!