Answer:
By performing experiments related with the elevation in boiling point and depression in freezing point.
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, we use the concept of colligative properties of solutions because they depend on the concentration of solute molecules or ions rather than its identity. They are classified as vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, freezing point depression and osmotic pressure.
Elevation in boiling point and depression in freezing point are suitable for us to determine the molecular formula of propane as shown below:
- Elevation in Boiling Point: by performing an elevation in boiling point experiment, it is possible to quantify ebuilloscopic constant for the solvent, in order words, the molal (referred to molality) boiling point elevation constant of propane, using it as a solute. Then, one applies the formula:
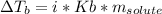
To compute the molality and subsequently propane's molecular mass.
- Depression in freezing point: by performing this one, it is possible to determine the molecular mass of the propane. Thus, we find the molal freezing point depression constant of the solvent to subsequently apply the shown below formula:
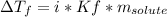
Which is suitable to compute the molality as well as in the previous case.
Best regards.