Answer:
The change in beam's length due to the thermal expansion is 0.00288 meters.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that,
Original length of the steel rod, l = 15 m
Initial temperature,
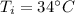
Final temperature,
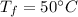
The coefficient of linear expansion of the steel,
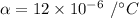
Let
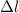 is the change in beam's length due to the thermal expansion. It can be given by :
is the change in beam's length due to the thermal expansion. It can be given by :
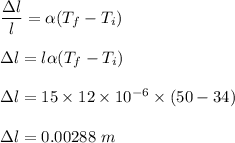
So, the change in beam's length due to the thermal expansion is 0.00288 meters. Hence, this is the required solution.