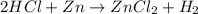Step-by-step explanation:
A chemical equation that contains equal number of atoms on both reactant and product side is known as a balanced equation.
For example,
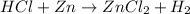
Number of atoms present on reactant side are as follows.
H = 1
Cl = 1
Zn = 1
Number of atoms present on product side are as follows.
H = 2
Cl = 2
Zn = 1
Therefore, to balance this equation we multiply HCl on reactant side by 2.
Hence, the balanced chemical equation is as follows.