Here we use the Pythagoras theorem
According to this, in a right angled triangle, the sum of the squares of the lengths of the two sides is equal to the hypotenuse
is "a" and "b" are the sides, and "h" is the hypotenuse, then :
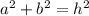
In the given problem, a = b = 12 and h = x
12^2 + 12^2 = x^2
So, x =
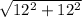
x =
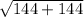
X =
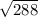
X = 12
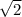 (Option B)
(Option B)