Since the events are dependent, the probability of occurrence of event B will impact the probability of occurrence of event A. So we will be using the formula of conditional probability to find P(A ∩ B).
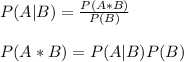
Here P(A*B) indicates P(A ∩ B).
Using the values, we get:
P(A ∩ B) = 0.25 x 0.4 = 0.1
Thus, option A gives the correct answer.