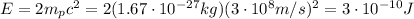The mass of the proton is:
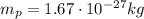
and the mass of the antiproton is exactly the same, so the total mass of the two particles is
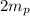
.
In the annihilation, all the mass of the two particles is converted into energy, and the amount of this energy is given by Einstein's equivalence between mass and energy:
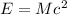
where M is the mass converted into energy and c is the speed of light. In this example,
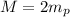
, therefore the energy released is