Answer:
y = x⁴ + x³ - 3x² + 5x + C
======
Separable differential equations such as these ones can be solved by treating dy/dx as a ratio of differentials. Then move the dx with all the x terms and move the dy with all the y terms. After that, integrate both sides of the equation.
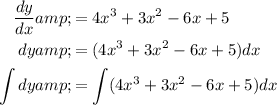
In general (understood that +C portions are still there),
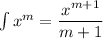
Note that ∫dy = y since it is ∫1·dy = ∫y⁰ dy = y¹/(0+1) = y
For the right-hand side, we use the sum/difference rule for integrals, which says that
![\int \big[f(x) \pm g(x)\big]\, dx = \int f(x)\,dx \pm \int g(x) \, dx](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/mathematics/college/6w9u3a62ypxkhpae4eqiz92vjsu58zr09y.png)
Applying these concepts:
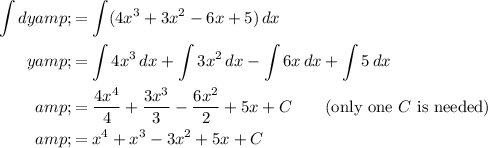
The answer is y = x⁴ + x³ - 3x² + 5x + C