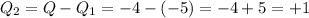Let's call Q the initial charge of the object, which is:
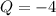
When it breaks, the two pieces will have charge
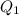
and
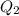
, and since the total charge must be conserved, the sum of these two charges must be equal to the initial charge of the object:
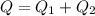
We also know the charge of one of the two pieces:
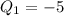
So, by substituting Q and Q1 into the equation, we can find the charge of the second piece, Q2: