Answer:
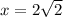 and
and
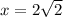
Explanation:
The given equation is
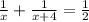
We need to solve the given equation.
Taking LCM on left side.
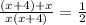
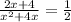
On cross multiplication we get
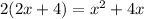
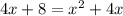
Subtract 4x from both sides.
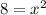
Taking square root on both sides.
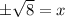
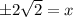
Therefore, solutions of the given equation are
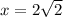 and
and
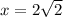 .
.