Answer:
Option A is correct
AAS theorem.
Explanation:
AAS(Angle -Angle-Side) theorem states that:
if two angles and any side of one triangle are congruent to two angles and any side of another triangle, then these triangles are congruent
In a given triangle ADB and CDB.
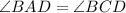 [Angle] [Given]
[Angle] [Given]
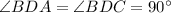 [Angle] [Given]
[Angle] [Given]
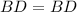 {Common side} [Side]
{Common side} [Side]
then by AAS theorem;
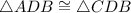
Therefore, ∆ADB ≅ ∆CDB by the AAS theorem.