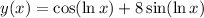Substitute
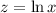
, so that
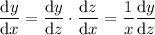
![(\mathrm d^2y)/(\mathrm dx^2)=(\mathrm d)/(\mathrm dx)\left[\frac1x(\mathrm dy)/(\mathrm dz)\right]=-\frac1{x^2}(\mathrm dy)/(\mathrm dz)+\frac1x\left(\frac1x(\mathrm d^2y)/(\mathrm dz^2)\right)=\frac1{x^2}\left((\mathrm d^2y)/(\mathrm dz^2)-(\mathrm dy)/(\mathrm dz)\right)](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/mathematics/college/dph34bzhne995cbn3s3iz7o1o5e3jluqpg.png)
Then the ODE becomes
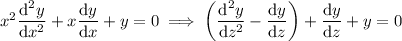
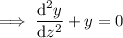
which has the characteristic equation
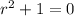
with roots at

. This means the characteristic solution for
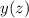
is
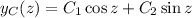
and in terms of
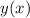
, this is
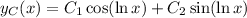
From the given initial conditions, we find
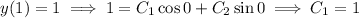
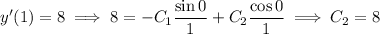
so the particular solution to the IVP is