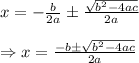The derivation of the quadratic formula is done using completing the square as shown below.
Given a quadratic equation:
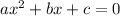
.
Make the coefficient of
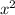
to be 1 by dividing through by a, to get
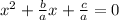
.
Next, take the constant term (the term with no x) to the other side of the equation to get
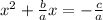
.
Then add to both sides of the equation, the square of half the coefficient of x, to get:
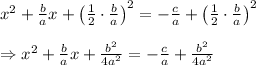
Next, we factorize the left hand side to get
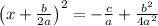
.
Then, we take the square root of both sides to get:
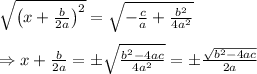
Finally, solve for x, to get: