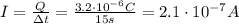The current in a wire is defined as the amount of charge that passes a given point of the wire in a given time:
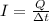
where Q is the charge and
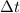
is the time interval.
Since one electron has a charge of
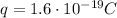
, the total charge of
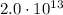
electrons is
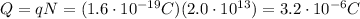
And since the time interval is
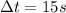
, the current in the wire is