The current is defined as the amount of charge Q that passes through a given point of a wire in a time
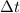
:
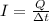
Since I=500 A and the time interval is
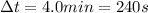
the charge is
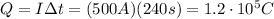
One electron has a charge of
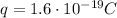
, therefore the number of electrons that pass a point in the wire during 4 minutes is
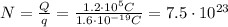
electrons