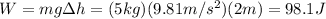The maximum amount of work that the hammer can do while falling to the ground is equal to its variation of gravitational potential energy, which is given by:
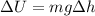
where m is the mass of the hammer, g is the gravitational acceleration, h is the variation in altitude of the hammer.
Plugging the data of the problem inside the equation, we find