Answer:
The first one among the four attached graphs correctly shows the effect on the freezing point caused by increasing the molality of a solution
Step-by-step explanation:
According to colligative property of molecules-
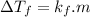
where
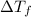 is the depression in freezing point
is the depression in freezing point
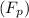
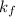 is cryogenic constant of solvent and m is molality of solution
is cryogenic constant of solvent and m is molality of solution
As
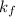 is constant for a certain solvent therefore the above relation is similar to linear equation y=mx. here y represents
is constant for a certain solvent therefore the above relation is similar to linear equation y=mx. here y represents
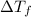 and x represents m
and x represents m
So a graph between
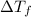 and m would give straight line passing through origin
and m would give straight line passing through origin
If we extrapolate the first graph by joining all the points then it will give a straight line passing through origin.
Hence the first graph is the correct one depicting change in freezing point with molality