Answer:
a larger current in the opposite direction
Step-by-step explanation:
As we know by Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction that rate of change in magnetic flux will induce electric current in a conducting coil linked with it
so it is given as
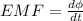
now in this situation we know that first a magnet is entering into the coil so here the magnetic flux is increasing linked with the solenoid coil.
So it will induce some current in the coil which shows deflection in galvanometer coil.
Now when we pull the magnet out then it will decrease the flux linked with the coil so here the direction of induced current must have to decrease.
Also it is given that coil is removed at faster rate due to which the rate of change in flux will be more so here it will induce more current
so correct answer would be
a larger current in the opposite direction