Answer : The reaction that is an example of oxidation reduction reaction is "Fe2O3 + 3CO yields 2Fe + 3CO2 "
Explanation :
The oxidation reduction reaction is the one in which one of the elements undergo oxidation and the other undergoes reduction.
The oxidation number of the element that undergoes oxidation increases .
The oxidation number of the element that undergoes reduction decreases.
Let us find out which of these reactions show an increase and decrease in oxidation numbers.
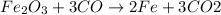
Let us find out the oxidation numbers of the elements involved in this reaction.
The standard oxidation state of O is -2
The overall charge on the compound Fe₂O₃ is 0.
Let us set up an equation to find oxidation number of Fe in Fe₂O₃.
2 ( oxidation number of Fe) + 3 ( Oxidation number of O) = Overall charge
2 ( oxidation number of Fe) + 3 ( -2) = 0
2 (oxidation number of Fe) - 6 = 0
oxidation number of Fe = 6/2 = +3
Oxidation number of Fe on reactant side is +3.
On product side Fe is present in its standard state. Therefore its oxidation number is 0.
Oxidation number of Fe on product side is 0.
Oxidation number of Fe changes from +3 to 0 which shows a decrease.
That means Fe undergoes reduction.
Let is find oxidation number of C on both the sides.
Oxidation number of C in CO is
oxidation number of C + (-2) = 0
oxidation number of C = +2
Oxidation number of C on reactant side is +2
Oxidation number of C in CO₂ is
Oxidation number of C + 2 x (-2) = 0
Oxidation number of C = +4
Oxidation number of C on product side is +4
Oxidation number for C changes from +2 to +4, which shows an increase.
Therefore C undergoes oxidation.
We can say that in the above reaction, one element ( Fe) undergoes reduction and the other (C) undergoes oxidation. This is an example of oxidation-reduction reaction.
Hence the correct option is "Fe2O3 + 3CO yields 2Fe + 3CO2 "