Answer:
A the first law
B the second law
C the third law
Step-by-step explanation:
All three Newton laws are involved in this example. Let's see why:
1) First Law: "an object which has a zero net force acting on it stays at rest if it was at rest or continue to move at constant speed if it was already moving" --> this law applies to the first part of the problem, before the launch, when the rocket is not moving: since no forces are acting on it, it stays at rest.
2) Second law: "a net force F applied to an object of mass produces an acceleration a given by the relationship:
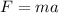 "
"
This law applies when the rockets starts its motion: in fact, a force of 44 N is applied to the rocket of mass 2.9 kg, and its acceleration is a=15.3 m/s^2, and we see that these numbers satisfy the previous equation.
3) Third law: "when an object A exerts a force on object B, object B exerts an equal and opposite force on object A"
This law applies when the rocket is in motion: in fact, the rocket pushes the hot gases outside, so the hot gases pushes back on the rocket, accelerating it so it moves forward.