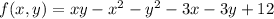
First compute the first-order partial derivatives and find the critical points.

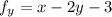
Both first order derivatives vanish at
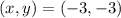
.
Computing the Hessian, we get
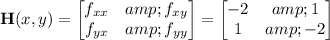
We have
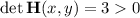
, which means
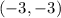
is an extremum of
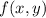
. Since
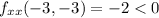
, this extremum is a local maximum of
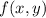
with a value of 21.