The amount of heat needed to increase the temperature of a substance by

is given by
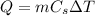
where
m is the mass of the substance
Cs is the specific heat capacity of the substance

is the increase of temperature of the substance
If we plug the data of the problem into the formula, we find
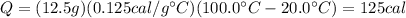
and this is the amount of heat needed to bring 12.5 g of aluminium from 20 degrees to 100 degrees.