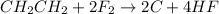Option 3: By removing hydrogen because of fluorine's attraction to hydrogen's nucleus.
The reaction of ethene and halogen generally breaks the carbon-carbon double bond and substitution of halogen on carbon takes place, this is known as halogenation reaction. This is in the case of reaction of ethene with chlorine, bromine and iodine. In the case of fluorine, due to high electronegativity it get attracts to the nucleus of hydrogen and form hydrogen fluorine gas. Therefore, halogentaion reaction do not take place in the case of ethene and iodine.
Ethene explosively reacts with fluorine to form carbon and hydrogen fluoride gas. The reaction is as follows: