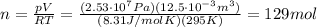The ideal gas law states that:
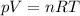
where
p is the gas pressure
V is its volume
n is the number of moles
R is the gas constant
T is the absolute temperature of the gas
For the gas in our problem:
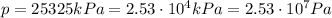
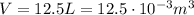
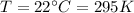
If we plug the data into the equation, we can find the number of moles of the gas: